This will be a very short post, because the only “new” information I’m going to provide is the minimal example to answer the question. Yes, it is in fact possible to call RSiteCatalyst from Python and seems to work well. The most important things are 1) making sure you install rpy2 and 2) loading Pandas (since so much of RSiteCatalyst is API calls returning data frames). It doesn’t hurt to already have experience using RSiteCatalyst in R, since all we’re doing here is using Python to pass code to R.
Setup Code: rpy2 and Pandas
To call an R package from Python, the rpy2 package works very well, both from the REPL and Jupyter Notebook. For RSiteCatalyst, here is the set up code:
1 | |
With this code run, now you can make calls to the RSiteCatalyst R package, just as if you were in R itself.
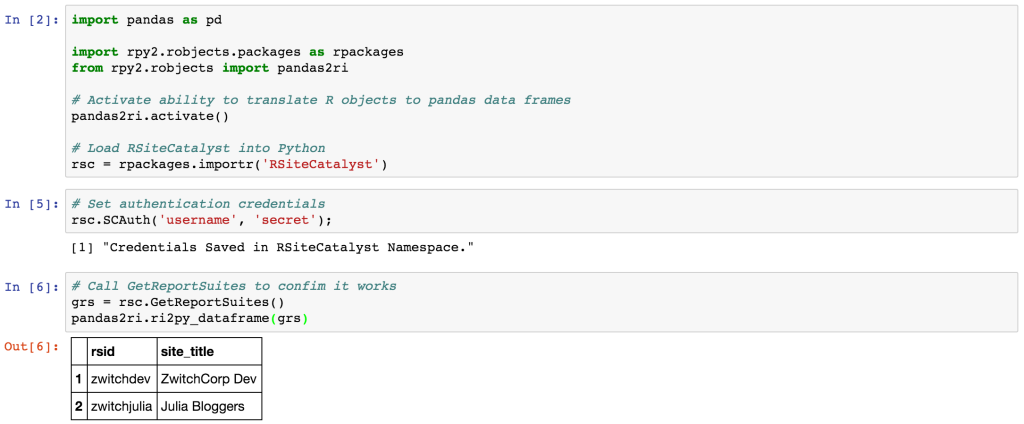
Sample Call: GetReportSuites
Just to prove it works, here’s a code snippet using GetReportSuites():
1 | |
And in Jupyter Notebook, you would see something similar to:
But, Why?
So that’s about it…if you wanted to, you could call RSiteCatalyst from Python without much effort. There aren’t a whole lot of reasons to do so, unless like Adam above, you’d rather just use Python. I suppose if you wanted to use some other Python packages, such as Flask to create a dashboard or Seaborn for visualization you might want to do this. Until I got this tweet, it never occurred to me to do this, so YMMV.
Edit, 2/26/16: Adam Gitzes, who originally asked the question, also provides a different solution using Jupyter Notebook magics at his blog post here