
In this article, we’ll take a moment to look at some of the interesting things that transpired in 2018 in the machine learning world. We’ll look at some of the top open source projects as ranked by Mybridge, major developments in machine learning frameworks, and some of the things to look forward to in 2019.
Top Open Source Projects
Let’s look at some of the top open source projects from the previous year
BERT
BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. BERT is a new method of solving natural language processing problems and obtains state of the art results. It’s based on TensorFlow and allows developers to solve problems using pre-trained models. BERT models have a big advantage over other models because they can identify the context in sentences. This project currently has 8841 stars and 1560 forks on Github. You can read the full academic paper here.
DeepCreamPy
This is a deep learning tool that reconstructs censored areas of an image just like an image editing tool (think Photoshop). One uses an image editing tool to color the censored areas in green, and the neural network fills those areas. The project currently has 6365 stars and 613 forks on GitHub.
TRFL
TRFL pronounced as truffle, is used to program reinforcement learning agents in TensorFlow. To try your hand at this, follow the documentation.
Horizon
Horizon is a platform for applied reinforcement learning. Horizon is built with PyTorch and uses Caffe2 for serving the model. A major advantage with Horizon is that it’s designed with production use cases in mind. To learn more about Horizon, check out the official paper at Facebook Research. If you’d like to try out Horizon you can check the documentation available here.
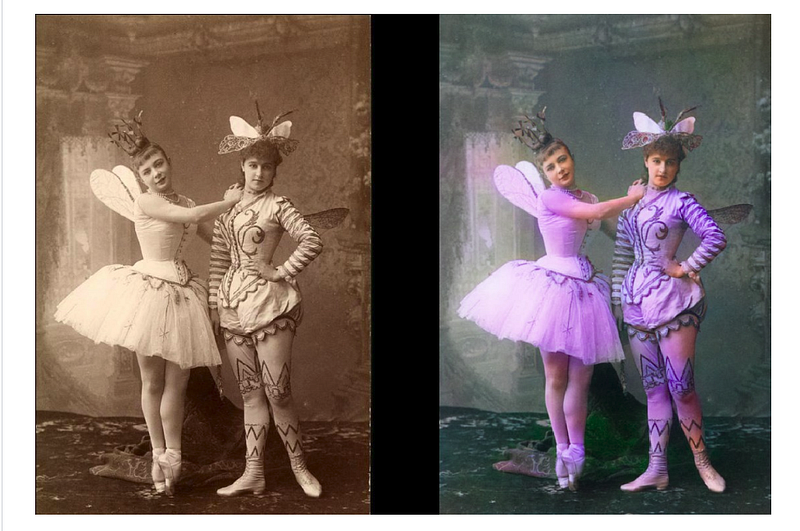
DeOldify
DeOldify, as the name suggests, is a deep learning library that colorizes and restores old images. The author has combined several approaches in order to achieve this. Namely, Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks, Progressive Growing of GANs, and the Two Time-Scale Update Rule. You can try it by heading over to this Notebook.
 Source
Source
AdaNet
AdaNet is a TensorFlow based library that automatically learns models without requiring a lot of expert intervention. The project is based on the AdaNet algorithm. To get started with AdaNet, head over to the official documentation.
Graph Nets
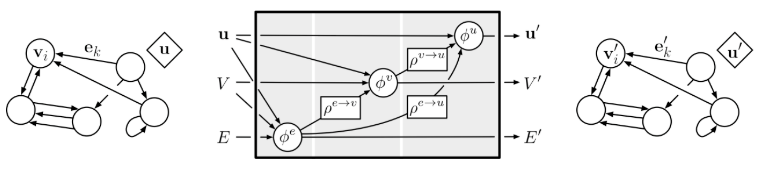 Source
Source
Graph Nets is DeepMind’s library for building graphs networks in Sonnet and TensorFlow. Graph networks take graph inputs and return graph outputs.
Maskrcnn-benchmark
This project helps in building object detection and segmentation tools in PyTorch. Some of the advantages of using this library are its speed, memory efficiency, Multi-GPU training, and inference, and it provides CPU support for inference.
PocketFlow
PocketFlow is a framework for accelerating and compressing deep learning models. It solves the challenge of computation expense experienced by most deep learning models. It was originally developed by researchers at Tencent AI Lab. To learn about its implementation check its official docs.
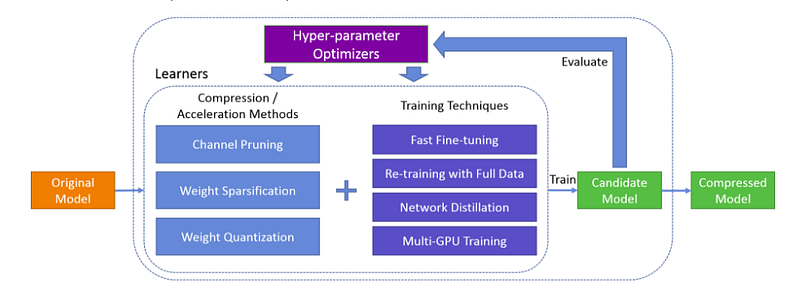 Source
Source
MAMEToolkit
MAMEToolKit is a library that trains reinforcement learning algorithms on arcade games. The toolkit receives gameplay frame data while tracking the state of the game.
 Source
Source
Major Developments in ML Frameworks
We’ll now look at a few developments in major machine learning frameworks.
PyTorch 1.0
In October during the PyTorch conference, Facebook released a preview version of PyTorch 1.0. The new version will solve the following challenges: time-consuming training, extensive networking, slow scale-up, and some inflexibilities caused by the Python programming language.
A set of compiler tools known has Torch.jit have been introduced in the new version. They will bridge the gap between production and research. Torch.jit includes a language known as Torch Script, a subset of Python. This will enable scripting of models from eager to graph mode. This will be very useful in developing high-performance and low-latency applications.
Auto-Keras
By now you’ve probably heard the phrase automated machine learning. Essentially, this means automating the process of searching the best parameters for your machine learning model. Other automated ML frameworks include Google’s AutoML. Auto-Keras is written using Keras and uses ENAS, a recent version of Neural Architecture Search.
TensorFlow Serving
TensorFlow Serving is a system that has made it easier to deploy TensorFlow models to production. While it was released in 2017, TensorFlow Serving has eased the work of developers this year, as far as moving models to production is concerned.
Machine Learning Javascript
There are a couple of Javascript frameworks that have popped up that allow developers to run their models on the browser. These include TensorFlow.jsand Keras.js. Model implementation is very similar to using the normal frameworks such as Keras or TensorFlow.
Looking Ahead
Looking forward into 2019 we can expect that developers’ work will be made easier with advancements in automation tools such as Auto-Keras. We can also expect the performance of various machine learning frameworks to improve because of advanced research and the contribution of the open source community.
I would also love to know some of your expectations in the machine learning space in 2019. Leave a comment below—let’s talk!
Bio: Derrick Mwiti is a data analyst, a writer, and a mentor. He is driven by delivering great results in every task, and is a mentor at Lapid Leaders Africa.
Original. Reposted with permission.
Related: