By Nils Schlüter, Software Engineer
Hyperparameter Tuning is one of the most computationally expensive tasks when creating deep learning networks. Luckily, you can use Google Colab to speed up the process significantly. In this post, I will show you how you can tune the hyperparameters of your existing keras models using Hyperas and run everything in a Google Colab Notebook.
Creating a new notebook and enable the GPU Runtime
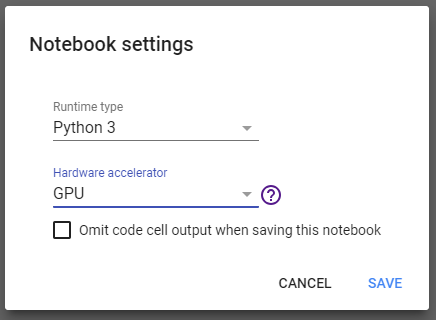 Dialog to change the runtime to GPU
Dialog to change the runtime to GPU
First, you need to create a new notebook. Open your Colab Console and select New Python 3 Notebook. In your notebook, choose Runtimefrom the menu and then Change runtime type. Select Hardware accelerator: GPU and hit save. This will significantly speed up every calculation you do in this notebook.
Installing the packages
You can install new packages using pip. In this case, we need hyperas and hyperopt. Copy and paste the following into the first cell of your notebook:
When you run the cell you will see that pip is downloading and installing the dependencies.
Getting the data and creating the model
For this post I’m going to use the example from the hyperas github page. You can find the finished Colab Notebook here.
**Data Function**
You’ll need a data function to load your data. It needs to return your X_train, Y_train, X_test and Y_test values. Here is an example for a data function:
Note:Your data function needs to return the values in exactly this order: X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test. Be careful if you’re using scikit learns train_test_split, as this returns the values in a different order
Note:Your data function needs to return the values in exactly this order: X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test. Be careful if you’re using scikit learns train_test_split, as this returns the values in a different order
**Model Function**
The Model Function is where you define your model. You can use your all available keras functions and layers. To add Hyperparameters for tuning, you can use the {{uniform()}} and {{choice()}} keywords.
Let’s say you want to try out different values for your batch_size. You can simply write batch_size={{choice([32, 64, 128])}} and during each trial, one of the values will be chosen and tried out . A more in-depth explanation on how to define the parameters to tune can be found on the Hyperas Github Page or you can look at the example:
Note:Your model function has to return a python dictionary with a loss key and a status key
Note:Your model function has to return a python dictionary with a loss key and a status key
Problems with Colab
If you try to run this example now, the trial will fail because Hyperas won’t be able to find your notebook. You need to copy your notebook and upload it again to your google drive folder. Luckily, you can do this from inside your notebook as described in this stackoverflow answer.
Note:In lines 16 and 18, you’ll need to change HyperasMediumExample to the name of your own notebook
Note:In lines 16 and 18, you’ll need to change HyperasMediumExample to the name of your own notebook
After running this cell, you will be prompted to open a website in your browser and copy & paste a code back into the notebook:
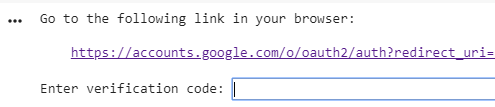 The output after you run the cell above
The output after you run the cell above
Follow the link, log in with your google account and copy & paste the code back into the notebook. If you open the FilesTab in the left sidebar, you should now see a File called
Starting the Trial
Now you can start the trial. Be careful, you have to set the parameter notebook_name to the name of your Notebook. Otherwise the Trial will fail:
After running this cell, the Scan starts you can see the result in the output of the cell.
Troubleshooting
If you have any problems while doing this, I recommend to do the following:
In the left sidebar, open Files.There will be a file called
After your runtime is connected again, you can start again by running every cell from top to bottom
Conclusion
With just a few tweaks you can use Google colab to tune the hyperparameters of your keras network. Again, the full example can be found here.
Bio: Nils Schlüter (@schlueter_nils) is a Software Engineer & Machine learning enthusiast.
Original. Reposted with permission.
Related:
